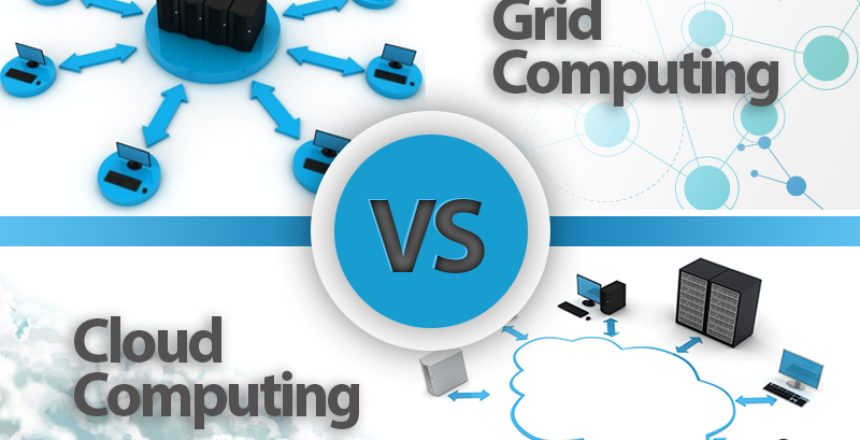
It is easy to get lost in the shuffle due to the many computing resource options available currently. Cloud Computing and Grid Computing are among some of the most popular buzzwords in the industry right now, and both have their advantages and use-cases. When asking yourself “Cloud Computing vs Grid Computing, Which is Best?” it is important to be able to understand the pros, cons, similarities, and differences of each. Read on for expanded explanations on all of the above and more…
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing Defined
Cloud computing is simply a method of storing and accessing data or software over the Internet rather than a local hard drive. “The Cloud” is tech jargon for a virtual, seamless connection. The term comes as a result of flowcharts and presentations that often visualize this virtual connection using a cloud.
READ MORE: What Defines a Cloud Service?
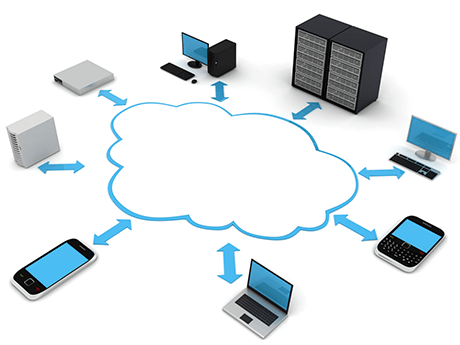
Utilizing Cloud Computing For Business and Developers
Currently, cloud services are used by developers and businesses of all sizes, all around the world. Furthermore, cloud services are a useful tool for businesses and developers. Cloud services allow for an affordable and reliable alternative to maintaining in-house servers. They can scale with a project’s needs while ensuring both security and uptime. Cloud computing allows for collaboration with team members and is easily implemented in projects of all shapes and sizes.
READ: Advantages to Turnkey Linux Applications and Self-Hosted VPS
Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing
Pros of Cloud Computing
- Disaster Recovery
With many services offering options such as regular backups and snapshots, important data loss is highly unlikely. - Increased Collaboration and Flexibility
Moving to the cloud increases opportunities for collaboration amongst employees. Colleagues can sync documents workflows or share apps with ease. Often these apps will allow collaborators to simultaneously receive updates in real time. Additionally, cloud computing allows for each team member to work from anywhere, at any time. The cloud centralizes data, meaning that business owners, employees, and clients can access company data from anywhere that has Internet access (this is often referred to as “tunneling-in”, via some sort of Remote Desktop Protocol). - Eco Friendly
Cloud computing can decrease a business’ carbon footprint, reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions by more than 30%. For small companies, the decreased energy usage can reach 90%! It can also help a business project an environmentally sound image.
- Disaster Recovery
Cons of Cloud Computing
- Internet Connectivity
Running business applications in the cloud is great, as long as a consistent Internet connection is maintained. If a cloud-based service provider loses connectivity, there’s not much to be done until that Internet connection returns. Even the best servers go down occasionally. Because of this, most cloud providers maintain several redundancies to ensure up time. It is important when selecting a cloud provider, to review their SLA. - Learning Curve
Cloud computing platforms are great tools for developers, but for newcomers to the industry, it might not be as simple as it seems. For those unfamiliar with Linux, SSH Key Generation, and other ins-and-outs of basic server administration, cloud computing platforms that deploy virtual machines or dedicated VPS (Virtual Private Servers) may seem much more different than what is anticipated.
What is Grid Computing?
Grid Computing Defined
At its core, grid computing is a computer network in which each computer’s resources are shared. Processing power, memory, and data storage are all community resources. Therefore authorized users can tap into and leverage these resources for specific tasks.
Grid Computing For Business and Developers
Grid computing allows for distributing jobs to many small server components using load sharing software. The software distributes the load evenly based on resources and policies. Now, instead of having one heavily burdened server, the load is spread evenly across many smaller computers.
Pros and Cons of Grid Computing
Pros of Grid Computing
- Cheaper Servers
No need to buy large SMP servers! Applications would be able to break apart and run across smaller servers. Those servers cost far less than SMP servers. - More Efficient
Much more efficient use of idle resources. Idle servers and desktops would be able to accept jobs! Many resources sit idle, especially during off business hours. This is not the case anymore with a grid computing setup. - Fail-safe
Grid computer environments are modular and don’t have just one fail point. Hence if one of the machines within the grid fails, there are plenty of others able to pick the load. Jobs can automatically restart if a failure occurs.
Cons of Grid Computing
- May Still Require Large SMP
Will be forced to run on a large SMP for memory hungry applications that can’t take advantage of MPI - Requires Fast Interconnect
You may need to have a fast interconnect between compute resources (gigabit ethernet at a minimum). Infiniband for MPI intense applications - Some Applications Require Customization
Applications would need tweaking to take full advantage of new models. - Licensing
Licensing across many servers may make it prohibitive for some apps.

Cloud Computing vs Grid Computing: Wrap Up
At face value, Cloud Computing and Grid Computing are very similar, but often serve very specific needs, projects and use cases. Cloud computing is great for flexibility, ease-of-use, and security, while Grid Computing makes utilizing physical hardware more economical when used in the right way. So, Cloud Computing vs Grid Computing, which is better? The answer really comes down to what you are trying to do and the resources you have at your disposal.
Click the link below to try a self-hosted VPS and to test a cloud platform and its pros and cons: